Dehydration in case of gastro: what to do?
Gastroenteritis , commonly called "gastro", is an infection that affects many people each year. Often resulting from a viral or bacterial infection, it disrupts the delicate balance of the digestive system , leading to a series of unpleasant symptoms such as nausea , vomiting , diarrhea and abdominal cramps . In cases of gastroenteritis, the rapid and frequent loss of body fluids can quickly exceed the body's ability to replenish them through habitual fluid consumption. This is especially true if appetite is reduced, which is common when suffering from gastrointestinal disorders. Additionally, the body's ability to effectively absorb fluids may be compromised during this illness, making fluid replenishment even more difficult. This is why drinking water and therefore rehydrating are essential aspects to give the body a sufficient supply of water after or during these episodes.
Identifying dehydration: symptoms and warning signs
What is dehydration?
Dehydration is a condition where the body loses more fluids and electrolytes than it receives. This is a particularly worrying phenomenon during gastroenteritis. This digestive condition, often accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea , significantly accelerates the loss of bodily fluids. These symptoms not only lead to water loss , but also a significant decrease in essential electrolytes like sodium , potassium , and chloride , which play a crucial role in maintaining normal bodily functions, including fluid balance, nerve transmission and muscle contraction.

In this context, it becomes imperative to quickly recognize the signs of dehydration to avoid potential complications. This is especially important in vulnerable populations, such as young children, the elderly and those with chronic illnesses, in whom the effects of dehydration may be more rapid and severe.
How to recognize dehydration?
Here are some signs and symptoms to watch for to identify and avoid dehydration:
Dry mouth and tongue: this is an early and significant indicator of dehydration, particularly in cases of gastroenteritis. This condition occurs when the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue lose their natural moisture and become noticeably dry and sticky. This unpleasant feeling is often accompanied by a reduction in saliva, which makes both swallowing and speaking difficult.
Reduced urinary frequency and dark urine: Normally, a healthy adult should urinate about six to eight times a day, but this frequency can decrease significantly when the body lacks fluids. This decrease in urinary frequency is a clear indicator that the body is trying to conserve the water it has, thereby limiting the amount of urine produced. When the body experiences dehydration , urine can take on a significantly darker shade, ranging from dark yellow to amber. This coloring is due to a higher concentration of wastes and chemicals, such as urea that the kidneys filter, from the blood. When the body is well hydrated, these wastes are diluted into more fluids, making urine clearer.
Unusual fatigue and lethargy: When the body lacks fluids, every cell and organ is affected, which can lead to feeling extremely tired, lack of energy and general weakness. Dehydration affects blood circulation and can reduce the supply of oxygen and essential nutrients to the muscles and brain. This can lead to a feeling of muscle weakness and decreased endurance capacity, making physical activities more difficult.

Dizziness or feeling light-headed: When the body loses a significant amount of fluid, blood volume may decrease, reducing the pressure the blood exerts on the blood vessel walls. This drop in blood pressure can cause insufficient oxygen and nutrients to reach the brain, causing dizziness or feelings of lightheadedness.
Our hydration advice during gastroenteritis
Drink liquids in small amounts
It can be difficult to consume large amounts of fluids at once. Opting to drink water in small, regular sips instead of drinking large volumes of water or other liquids all at once helps gently reintroduce fluids into the body without risking worsening symptoms like nausea or vomiting. Clear soups, vegetable broths, herbal teas can help you. And we also find Hydratis solutions which will contribute to rehydration , while providing essential electrolytes which can be lost in cases of gastro. Water-rich fruits, like watermelons or peaches, can also be sources of hydration , while also being gentle on the digestive system .
Use of Hydratis rehydration solutions

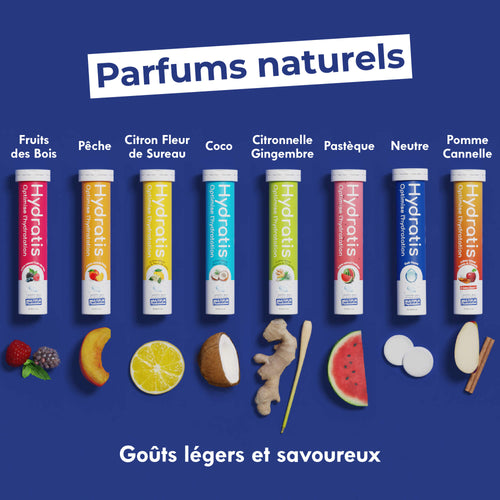
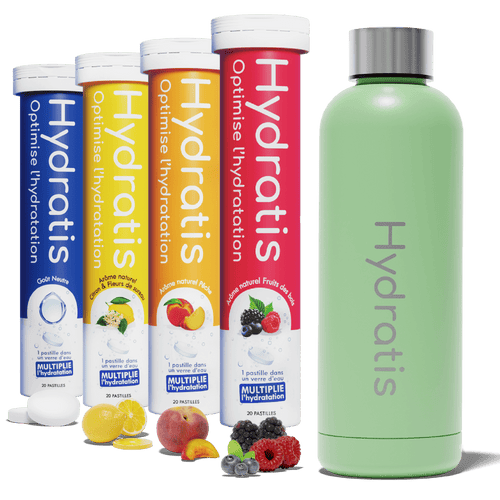
Hydratis is a rehydration solution specially designed to meet the needs of people suffering from fluid and electrolyte imbalances, as is often the case with gastro. Indeed, these carefully developed solutions offer a rich and optimal blend of salts, sugars, and minerals which ensure rapid and effective absorption of water, allowing rapid rehydration without overloading or further irritating the system. digestive. Our products are formulated to give a precise balance between hydration and flavor, making them more pleasant to consume while being effective in reboosting the body! As for its use, we advise you to put one tablet in 250ml of water and take small quantities regularly, to be renewed throughout the day as soon as you feel the need (eg: every 2-3 hours).
Avoid certain drinks
Caffeinated beverages, such as coffee, tea, and some sodas, as well as very sugary sodas and fruit juices, can often make diarrhea symptoms worse and, therefore, exacerbate dehydration.
Daily prevention and hydration
Preventing dehydration is a crucial aspect of overall health that goes far beyond managing periods of illness. Indeed, adequate daily hydration plays a fundamental role in maintaining optimal health and contributes to many aspects of physical and mental well-being. Insufficient fluid intake can lead to a variety of health problems, from fatigue and difficulty concentrating to more serious problems like kidney stones or hypotension . If there are signs of severe dehydration or if symptoms persist, medical consultation is essential.
Vigilance for signs of dehydration and the application of appropriate hydration strategies play a crucial role in the effective management of gastro. Following these water losses, we recommend drinking regularly throughout the day, not just in response to thirst, which is often a late sign of dehydration! Our oral rehydration solutions are designed to help maintain optimal fluid balance , especially for active people or those living in hot climates where fluid loss may be accelerated. We are committed to helping everyone achieve this vital electrolyte balance, by encouraging healthy hydration practices and providing quality products to support this goal. We will meet you at the pharmacy or on our website hydratis.co and don't forget to hydrate :)
Bibliography
National Library of Medicine. June 12, 2023. “Viral Gastroenteritis” - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518995/
Ameli. October 27, 2023. “Gastroenteritis in adults: what to do? » - https://www.ameli.fr/assure/sante/themes/gastro-enterite-adulte/bons-reflexes-que-faire
Ameli. December 6, 2023. “Dehydration” - https://www.ameli.fr/assure/sante/urgence/pathologies/deshydration
National Library of Medicine. October 3, 2022. “Adult Dehydration” - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555956/
Science Direct. September 21, 2023. “Emergency department assessment and management of children with gastroenteritis” - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2588994X23000696?via%3Dihub