This store requires javascript to be enabled for some features to work correctly.
mon panier
✕Plus que 35,00 € pour profiter de la livraison offerte
Vos produits offerts seront ajoutés au panier automatiquement.
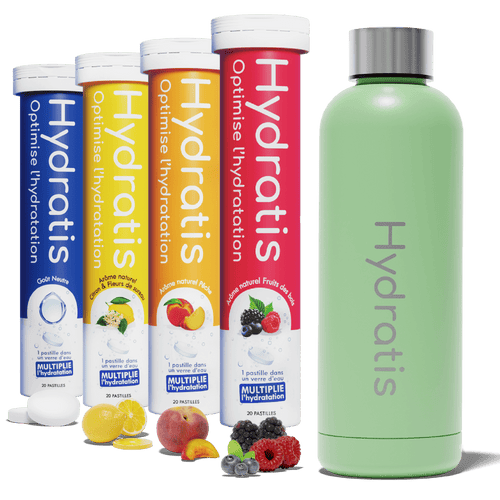
Nos produits
Nos produits
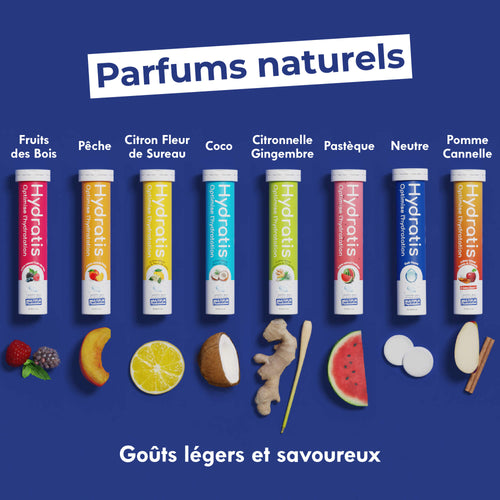
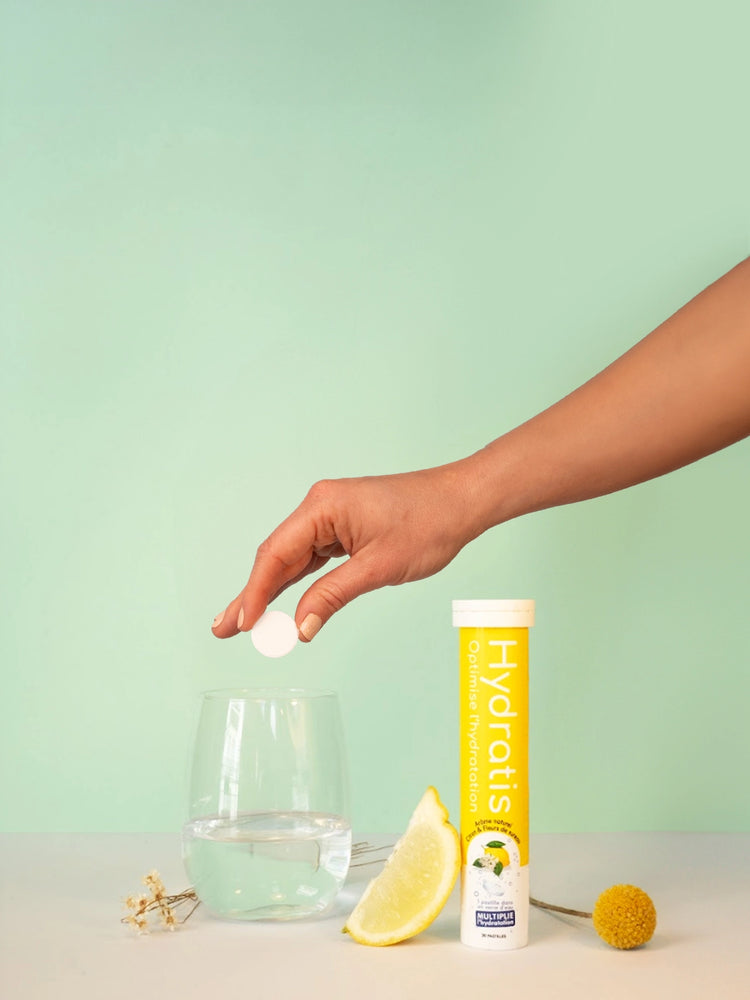
Votre solution d'hydratation pour chaque moment de vie
Le corps humain est composé à 60% d'eau. Être déshydraté c’est être privé de carburant VITAL. Découvrez comment Hydratis s'adapte à chaque moment de votre vie afin de transformer votre eau en élixir de vie.
Votre solution d'hydratation pour chaque moment de vie
Le corps humain est composé à 60% d'eau. Être déshydraté c’est être privé de carburant VITAL. Découvrez comment Hydratis s'adapte à chaque moment de votre vie afin de transformer votre eau en élixir de vie.
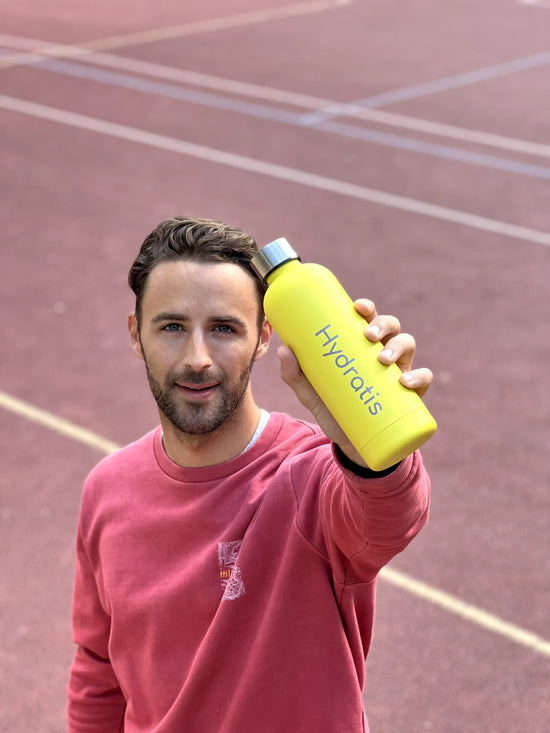

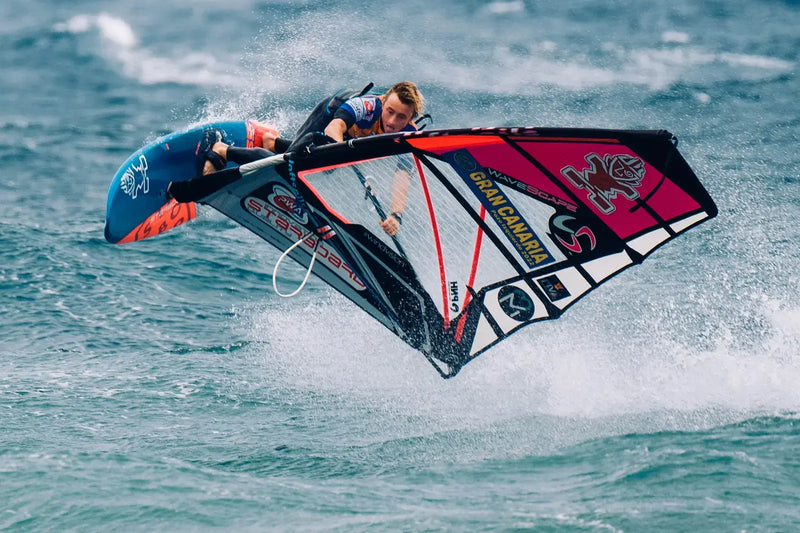
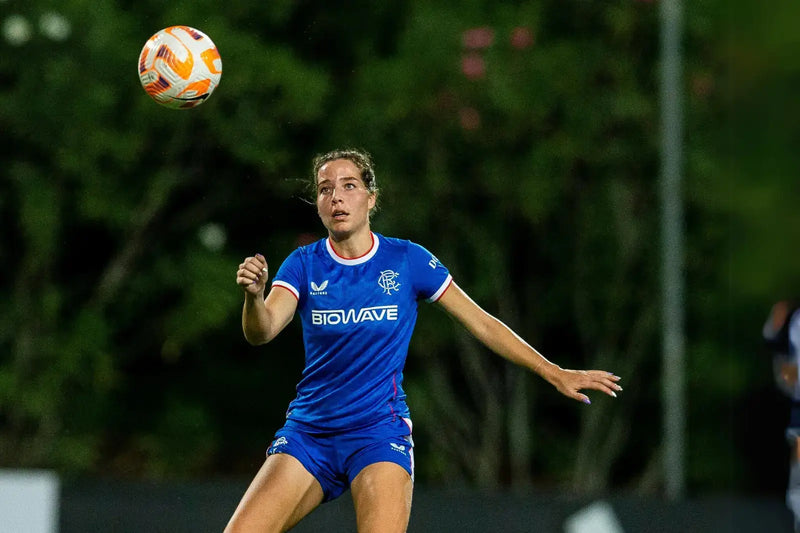
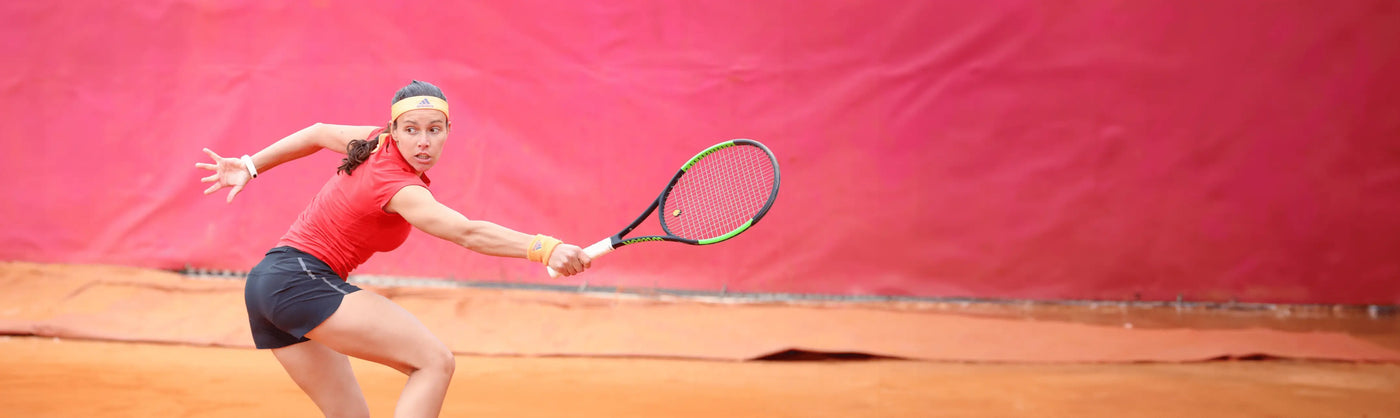
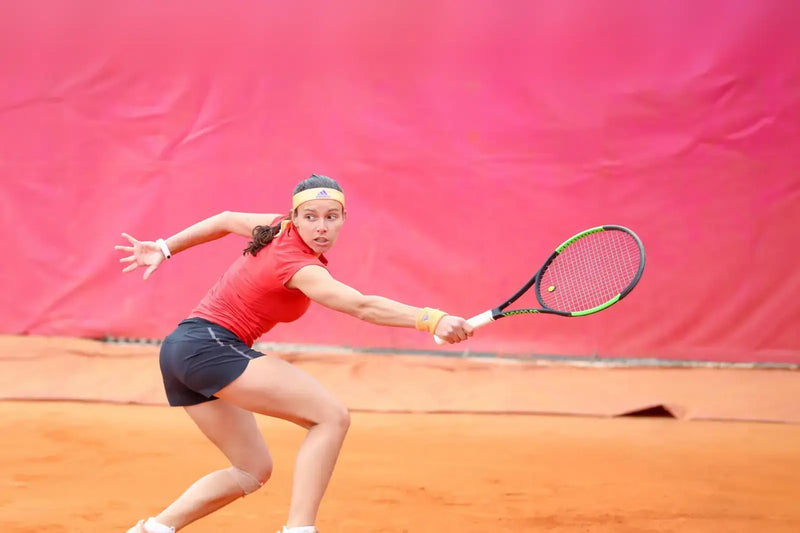
Améliorez vos performances et récupérez plus rapidement
Lorsque vous transpirez, vous perdez les 6 minéraux qui vous permettent d’être performant. Avec Hydratis, combattez la déshydratation, boostez votre énergie et améliorez votre récupération. Vous n’êtes qu’à quelques gouttes de vos meilleures performances.
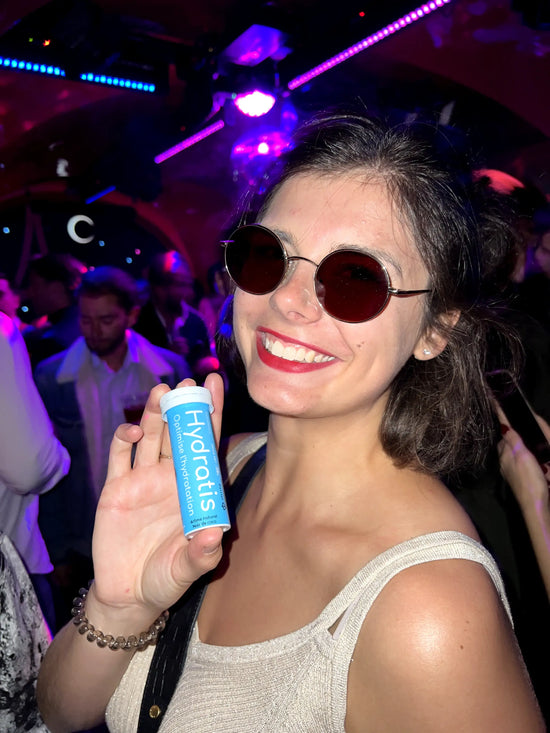

Évitez la veisalgie
Il faut savoir que l'alcool est un diurétique, c'est-à-dire qu'il augmente la production d'urine et donc déshydrate. On estime qu'en buvant 4 verres de vin, l'organisme perd 1 L d'eau !
Combattez la déshydratation, évitez la gueule de bois et réveillez-vous frais et dispos. Faites de Hydratis votre dernier verre de la soirée !
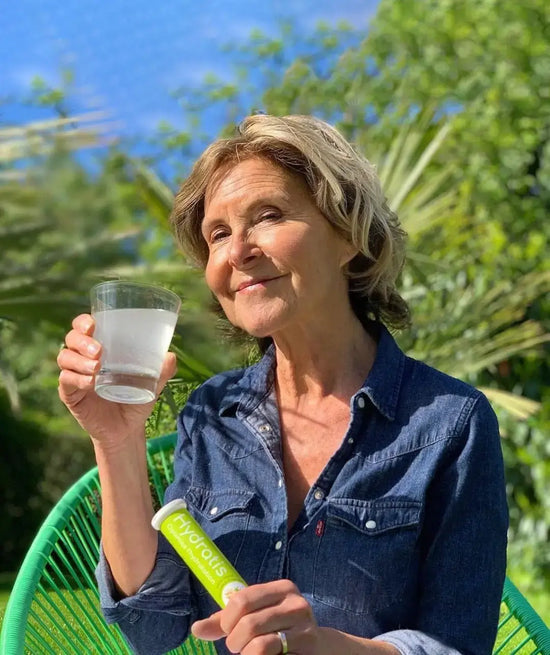

Combattez la déshydratation au quotidien
L'hydratation est vitale pour les seniors, aidant à éliminer les toxines et réguler la température corporelle. Avec l'âge, le risque de déshydratation augmente. Hydratis facilite une hydratation adéquate, soutenant la santé et le bien-être des aînés.
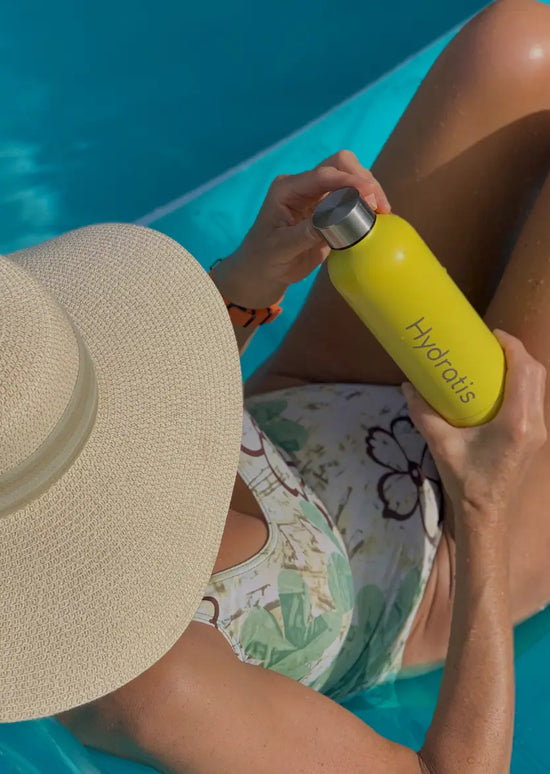

Débloquez l’énergie d’accomplir plus
3 personnes sur 4 ne boivent pas assez d’eau au quotidien, entraînant fatigue et manque de concentration. Hydratis vous permet d’avoir une hydratation de meilleure qualitée pour une source d'énergie et de bien-être. Faites que chaque gorgée compte pour une vie plus saine et plus éclatante.
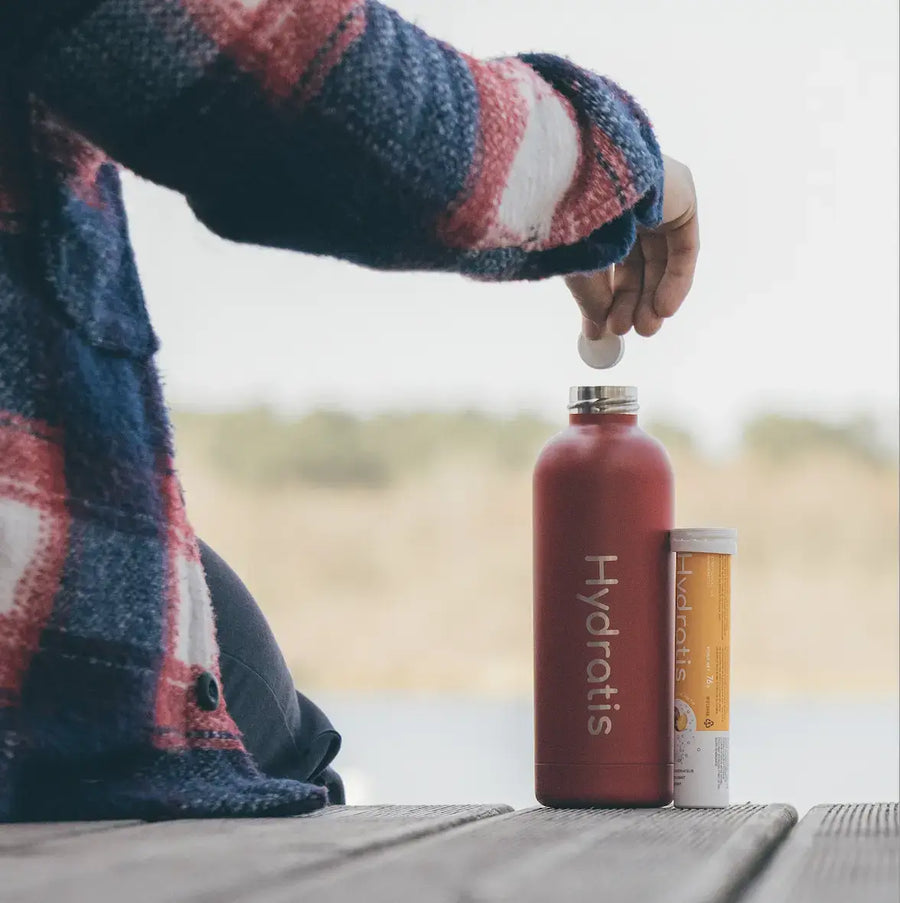

Hydratez votre quotidien
Vivez pleinement chaque instant en adoptant une hydratation maximisée, facile et agréable.
Que vous soyez aventurier dans l'âme, sportif passionné, voyageur avide de découvertes, professionnel dans des environnements intenses, fêtard ou tout simplement en quête d'une meilleure hydratation au quotidien, Hydratis sera votre allié.
Libérez votre soif d'aventure avec Hydratis !
Découvrir nos produitsCe n'est pas de la magie, mais de la science !
Hydratis a été créé avec un cabinet scientifique français, sa formulation permet de multiplier l'hydratation du corps et de gagner en énergie. Hydratis est approuvé par les professionnels de santé et est aussi utilisé par des athlètes et des pompiers.